A new company called Ocean Power Grid Inc. will be established in the third quarter of 2023 to advance the maritime power transmission business using Battery Tankers. The company will own, sell and operate battery tankers in Japan and internationally. PowerX is seeking business partners worldwide for this new technology and business initiative.
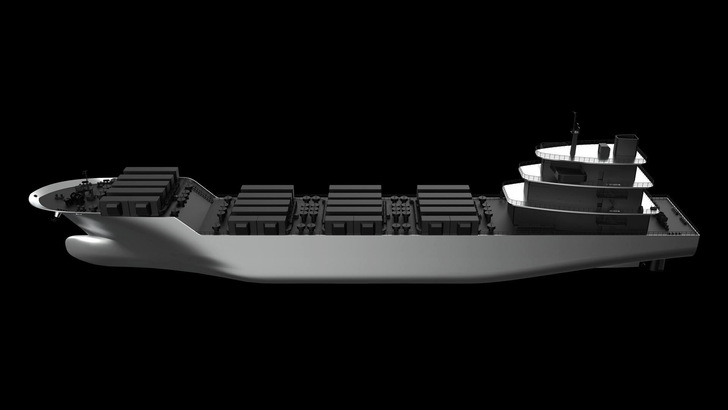
The first Battery Tanker is scheduled for domestic and international field testing from 2026. The 140-metre electric propulsion vessel will be fitted with 96 containerised marine batteries, delivering a total capacity of 241 megawatt hours.
System scalable for even larger vessels
The onboard battery system uses a proprietary module design and incorporates lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cells with a lifespan exceeding 6,000 cycles. The system is highly scalable, enabling the installation of additional batteries to create larger electric transport vessels such as the Power Ark 1000 or even larger, depending on operational needs. Dedicated gas emission control and fire suppression mechanisms are included to ensure safety, while real-time monitoring of the battery system, charging controllers and power conversion systems further strengthens safety measures.
Electric hydrofoil ferry to operate in Northern Ireland by 2024
All batteries will be manufactured in Okayama Prefecture, Japan, and are scheduled to obtain international ship classification certifications and standards such as DNV and Class NK. They will undergo rigorous testing to meet the strictest requirements. Delivery is set to begin by mid-2024.
The role of the battery tankers
The onboard battery systems enable Battery Tankers to store and transport surplus electricity generated from renewable sources. Decommissioned or idle thermal power plants near ports can be retrofitted as charge and discharge points, allowing power to be transferred to users through onshore grid connections and supporting more effective use of renewable energy.
Areas with high renewable energy potential are often far from urban centres and regions with high power demand, making robust transmission infrastructure essential. Given the current energy density of lithium-ion battery cells, Battery Tankers offer an effective solution for short-distance maritime power transmission between land points, complementing existing interregional grid connections.
Is hydrogen the 850-billion-dollar green game everybody wants to play?
A practical solution for seismically active areas
Battery Tankers will create new power transmission networks across the sea, supporting renewable energy storage, supply and utilisation. As battery energy density increases and costs decline, longer-distance maritime transmission from offshore wind farms to shore is expected to become feasible.
Battery Tankers provide a practical solution for regions prone to earthquakes and surrounded by deep seas. This ship-based approach avoids extended downtime caused by undersea cable failures and reduces the high costs linked to ultra-high voltage connections and substations.
As a result, Battery Tankers will make it possible to install offshore wind farms in locations where undersea cable deployment is difficult. Maritime power transmission using Battery Tankers can help overcome key challenges facing offshore wind and support the broader adoption of renewable energy worldwide. (mfo)