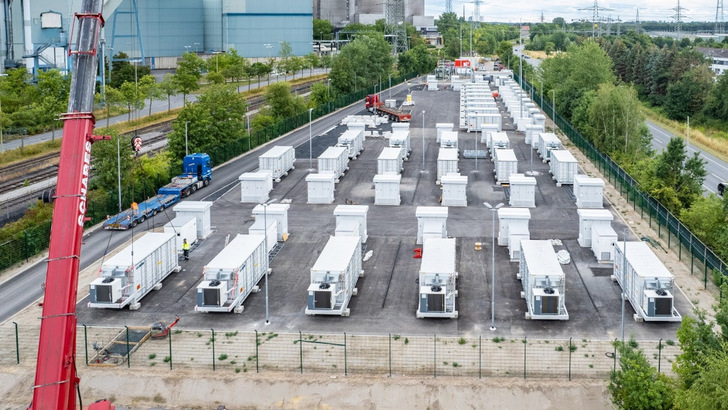
BNEF forecasts that global energy storage additions will reach 92 GW or 247 GWh in 2025, excluding pumped hydro. This marks a 23 percent increase in gigawatts over 2024, reflecting robust growth across established and emerging markets. While China and the US remain leaders, countries such as Germany, the UK, Australia, Canada, Saudi Arabia and regions like Sub-Saharan Africa are also accelerating deployment this year and next. Looking ahead, global installations are set to climb to 123 GW or 360 GWh in 2026, representing a 33 percent year-on-year increase.
6.9 TWh of new capacity by 2035
Between 2025 and 2035, cumulative energy storage installations are projected to add 1.9 TW or 6.9 TWh of new capacity, alongside 8.7 TW of new solar and 2.0 TW of new wind. In China and the US, recent policy shifts are expected to slow the pace of new solar and wind projects, but storage deployment should remain strong as market players adjust to changing conditions. By the late 2020s, markets such as India, Southeast Asia, Italy and Latin America are set to ramp up deployment. By the end of 2035, BNEF expects cumulative storage capacity to reach 2.0 TW or 7.3 TWh – twelve times the total installed in 2024.
Rolls-Royce – managing complexity in large-scale storage
Larger share for long-duration storage
Utility-scale projects are set to account for 84 percent of annual gigawatt-hour additions in 2025. Through 2028, short-duration energy storage – specifically projects with less than six hours of capacity – will make up around 80 percent of total installations by gigawatt-hours. Later in the decade, long-duration energy storage (more than six hours) will gradually claim a larger share as deployments increase in markets such as Australia, the US, Canada, the UK, Japan, South Korea and Italy. Notably, lithium-ion battery systems are now being extended to six-to-eight-hour projects in these regions, putting them in direct competition with other emerging long-duration storage technologies.
Navigating hurdles in large-scale battery project finance
Falling LFP prices
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is expected to retain its dominant market share over the next decade, driven by lower costs and longer cycle life, further pressuring nickel-based battery chemistries. LFP’s share is projected to peak at 93 percent in 2027 before gradually declining as a wider range of technologies, including long-duration energy storage, enter the market from the late 2020s. Falling LFP prices are also likely to constrain the expansion of sodium-ion batteries.
Solar Investors Guide #2 – Storage for revolutionising the grid
EMEA surpasses the Americas
Annual energy storage installations in Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA) are expected to overtake those in the Americas from 2026. In Europe, mature markets like Germany and the UK will continue to grow, while Italy’s new auction programme will drive further capacity additions after 2030. In the Middle East, Saudi Arabia is scaling up deployment, supported by state utility procurement and declining storage costs. Across Africa, rising battery imports are helping to spur market uptake. By 2035, cumulative EMEA deployment is projected to reach 516 GW or 1,564 GWh. (hcn)