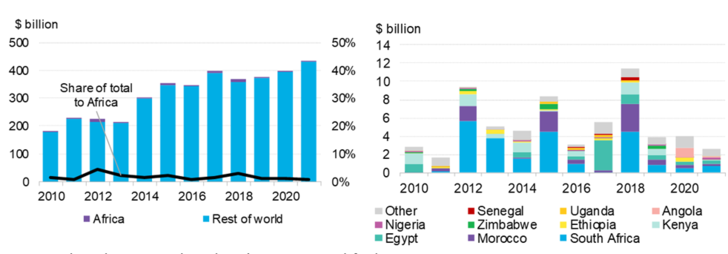
Despite Africa’s outstanding natural resources, rapidly growing electricity demand and improving policy frameworks, only $2.6 billion of capital was deployed for new wind, solar, geothermal or other renewable power-generating projects in 2021, the lowest in 11 years. The continent accounted for just 0.6% of the $434 billion invested in renewables worldwide.
The poor results cannot be blamed on any lingering effects of the Covid-19 pandemic. While renewables investment globally rose 9% from 2020 to 2021 to reach an all-time high, renewables investment in Africa slipped 35% year-on-year.
“The global transition from fossil fuels to clean energy has the potential to benefit economies and health across Africa,” said Michael R. Bloomberg, UN Secretary-General’s Special Envoy on Climate Ambition and Solutions and Founder of Bloomberg LP and Bloomberg Philanthropies. “But as this new report details, clean energy investment in Africa is at an alarming low level. Changing that requires new levels of collaboration to identify viable clean energy projects and bring more private financing and public support to them – so we can turn Africa’s potential as a global clean energy leader into reality.”
Just 5 % power share of wind and solar – investments concentrated
The new BloombergNEF report examines the opportunities and challenges for clean energy deployment in Africa. Available on the Bloomberg NetZero Pathfinders platform – a public resource supported by Bloomberg Philanthropies that provides concrete, actionable policy ideas for achieving a decarbonized economy – the study found that clean energy investment in Africa is highly concentrated in a handful of markets. South Africa, Egypt, Morocco, and Kenya have accounted for nearly three-quarters of all renewable energy asset investment since 2010 with a total of $46 billion. All others have secured just $16 billion over that time.
Also interesting: PV plants and added value for Kalenjin Tribes in Kenya
Africa lags far behind the rest of the world in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 7 of having clean, affordable energy for all its citizens. Among all those lacking access to electricity globally, 77% or 564 million reside in sub-Saharan Africa, according to the World Bank. Renewable technologies are cost-competitive today in most parts of the world, but particularly in Africa due to the continent’s wealth of natural resources. These resources have the potential to be transformative in expanding power-generating capacity and access to electricity on the continent. Nevertheless, 75% of Africa’s power needs are met today by coal- and natural gas-fired generation. Wind and solar accounted for just 5% of generation in 2021.
Ambitious targets – but weak implementation
In addition, countries in the region have made noteworthy strides to improve their policy regimes with an eye toward attracting funding for clean energy projects. Among the 42 African nations BNEF surveyed for its study, 86% now have long-term clean power targets in force, up from 57% in 2019. Net metering policies, which allow owners of distributed solar systems to be compensated for excess generation they feed back into the grid, are in place in 29% of African nations.
However, countries have done far less to implement concrete programs to ensure that they meet their long-term clean energy targets. While half the nations that BNEF surveyed have policies in place to hold reverse auctions for clean power delivery contracts, far fewer have held tenders. Even fewer have successfully brought projects online under such auctions.
“The ingredients are there for Africa to be a major market for clean energy growth, including outstanding natural resources and massive demand,” said Luiza Demôro, head of energy transition research at BNEF. “But incomplete policy regimes and reluctant investors continue to keep investment levels below where they could and really should be.” (hcn)
Did you miss that? Lay foundations for Africa’s clean energy future